The EBARA Group's Strategic Table of Common Basic Technological Capabilities
The EBARA Group has reorganized into five in-house companies to handle each of its target markets.
Accordingly, we revised the EBARA Group Strategic Table of Technological Capabilities to show the core technologies that constitute the competitive edge of each of the five in-house companies, the shared technologies between the companies, and the common basic technologies.
We will utilize these technologies to contribute to society with passion and dedication.


Chemical Analysis
In addition, EBARA supports product development in all business units by conducting water quality analysis to select optimal materials for the usage environment, and cross-sectional observation, fracture surface observation, and foreign matter analysis to elucidate the degradation mechanism.


Assembly
EBARA possesses the assembly technology necessary to ensure product performance, such as centering for large products such as large-scale pumps, compressors and turbines, and gap adjustment for vacuum pump products.

Casting
EBARA is actively working to digitize casting processes. Based on 3D models created by our design department, EBARA is developing high-quality casting manufacturing technology and applying it to our products by digitizing a series of processes, including preparation of casting plans using 3D-CAD, preliminary evaluation of quality with casting simulations, cast manufacture using sand mold 3D printers, and post-casting quality inspections using 3D scanners.

Industrial Engineering
Based on the Toyota production system concept, EBARA conducts work analysis and flow analysis using industrial engineering (IE) to improve production lines in order to ensure efficient production at plants. We are also working to improve layouts using production simulators.


Machining
EBARA uses various measuring instruments to determine machining conditions such as cutting power, and to observe tool cutting edges. We also use machining simulation technology to optimize machining conditions.

Presentational Maintenance
EBARA uses IoT to collect operating information from machine tools and factory utility equipment in order to monitor their operating status. These data are used to determine equipment times and operating rates, as well as to detect abnormalities and carry out preventative maintenance.

Production System
A manufacturing execution system (MES) is used to monitor progress on the production floor and issue instructions to workers.

Press Working
These welding technologies are subject to quality control in accordance with welding standards such as ASME. EBARA is also working on welding automation using robots, welding cameras, and sensors.

Chemistry
EBARA possesses technical knowledge on material surface treatment (chemical modification, coating, silane coupling treatment, plasma treatment, polymer brush treatment, micro-fabrication, etc.) to contribute to improvements in product performance, such as corrosion prevention and sliding, adhesion and bonding, and wettability control.

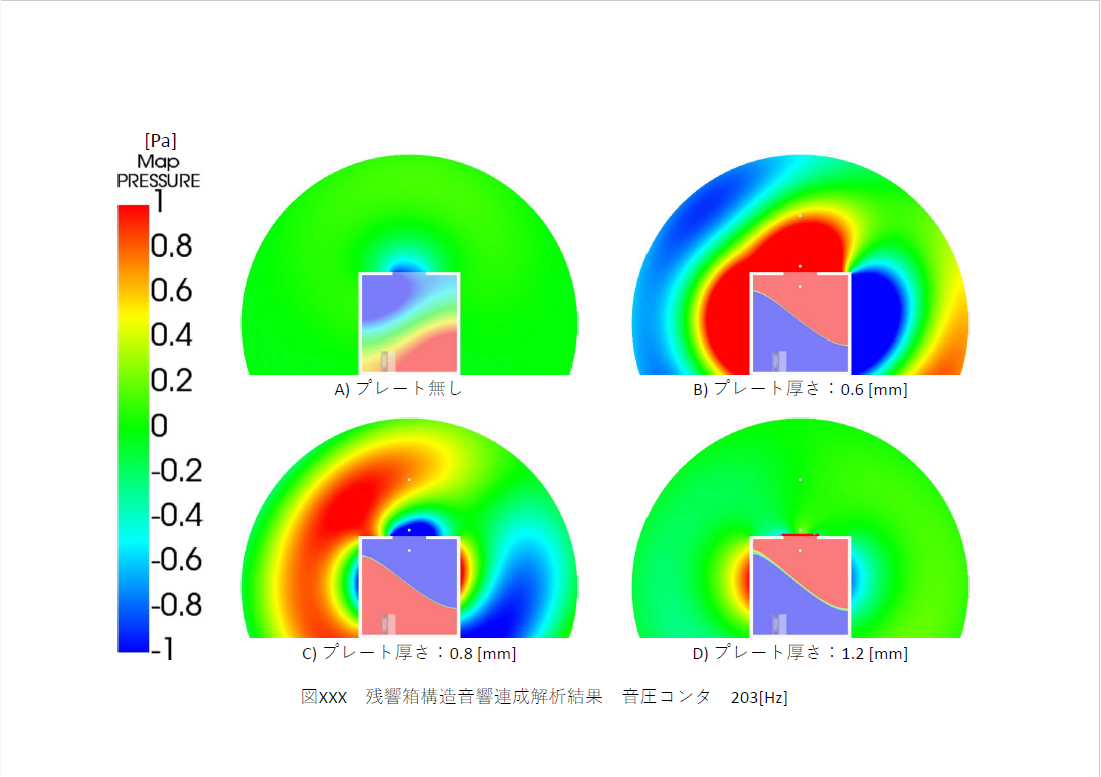
Vibration & Acoustics
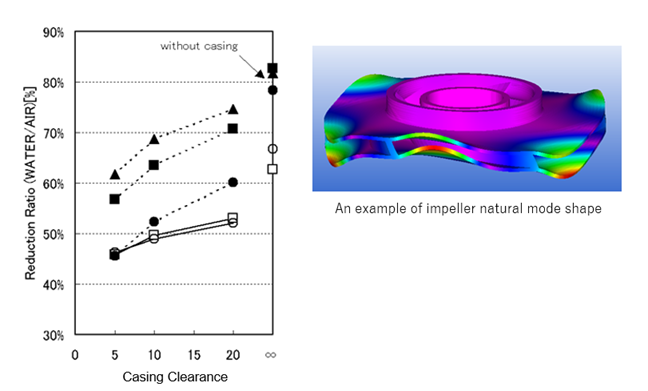

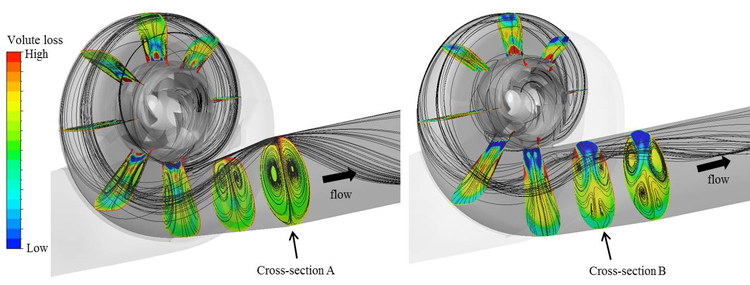
Fluid
EBARA possesses development and design technology for highly efficient products by analyzing the internal flow of fluid machinery, as well as maintenance technology for predicting damage through cavitation analysis, measurement technology for fluids, visualization technology for fluids using PIV and oil film methods, and advanced fluid dynamics analysis technologies applicable to EBARA products in order to improve the development, design, and reliability of products.

Heat Technology
In order to contribute to the development of products utilizing heat transfer such as chillers, cooling towers, and geothermal power generation,EBARA has technologies for measuring and estimating the amount of heat transfer from applicable objects to the environment.


Motion Control

Material
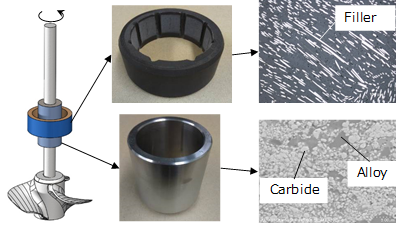
EBARA possesses basic technologies and application techniques for corrosion protection of metallic materials, as well as sliding and wear and structural strength of metallic materials and plastic materials in order to contribute to the selection of EBARA product materials used in specific environments, the prediction of product life, and the improvement of product reliability.

Numerical Analysis
EBARA provides support for product development in all business units by utilizing a wide range of analysis technologies, including thermo-fluid analysis, structural analysis, vibro-acoustic analysis, mass transfer analysis, coupled analysis that combines these methods, multiphase flow analysis such as cavitation analysis, molecular dynamics analysis, as well as large-scale computing technologies that use powerful computers with several thousand cores, and data science technologies such as data assimilation.
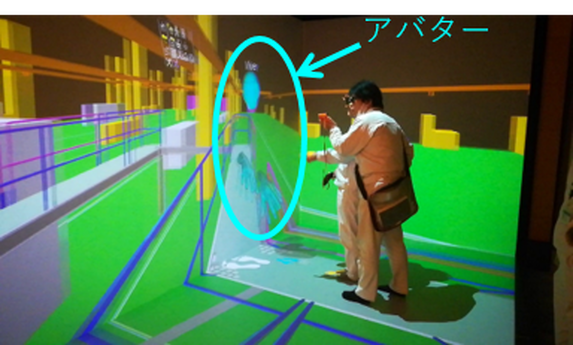
Extended Reality
EBARA applies virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies, as well as technologies that utilize high-speed communication, the cloud, and AI for these xR technologies to enhance and improve the efficiency of various internal operations.

Data Science
EBARA possesses the technology (data collection, processing, tabulation, visualization, analysis, model creation, AI, etc.) necessary to extract new value from data and solve problems for which no theories have yet been formed, or for which it is difficult to obtain explicit knowledge.

Additive Manufacturing
EBARA possesses additive manufacturing technology using metal 3D printers (beam conditions and support design for each material) and deformation prediction analysis technology. These technologies contribute to the rapid supply of parts, integration of multiple parts, and the efficiency of design and prototype testing through topology optimization. EBARA is also promoting the use of 3D printers in sand mold manufacturing for castings and in lost resin pattern casts for precision casting.

Welding
EBARA possesses welding technology that requires high quality, such as that used in the welding of extremely thick plates with thickness greater than 100 mm (compressor bodies, etc.), and in the welding of highly corrosion-resistant materials such as duplex stainless steel for seawater pumps.
These welding technologies are subject to quality control in accordance with welding standards such as ASME. EBARA is also working on welding automation using robots, welding cameras, and sensors.


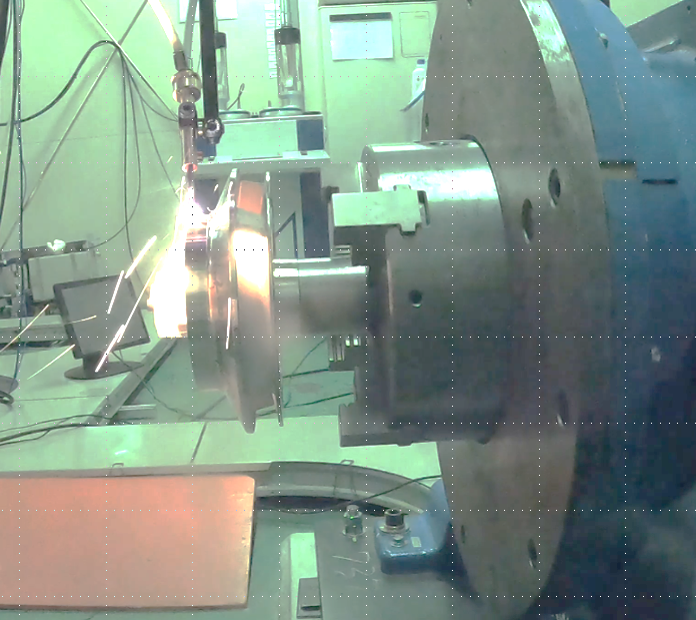
Thermal Spray
Surface treatment technologies such as thermal spraying and laser cladding are used to give corrosion resistance and wear resistance to pump impellers and shafts. These techniques are also used to restore the shape of damaged parts.

Reverse Engineering
EBARA possesses the technology to create 3D data by performing 3D scans and dimensional measurement of actual objects for repair and replacement of parts that are old and have no drawings or other companies’ products. This 3D data allows us to optimize designs and quickly produce parts using additive manufacturing technology.

Non Destructive Testing
To confirm the soundness of our products, EBARA uses non destructive examination (NDE) techniques such as penetrant testing (PT), magnetic particle testing (MT), ultrasonic testing (UT), and radiographic testing (RT). We are also working to digitize NDE techniques.

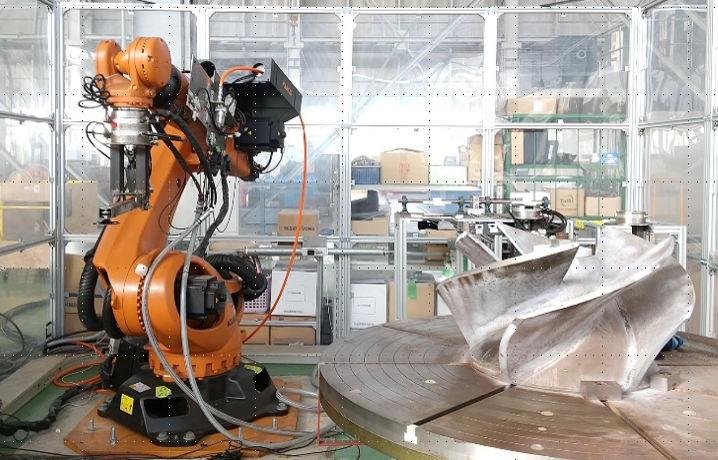
Robot
EBARA actively promotes the use of robots in manufacturing processes. We also promote their use in automated vacuum pump and standard pump assembly lines, as well as in welding, coating, and grinding processes.
