Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations 2021
Endorsement of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and Our Corresponding Efforts
The global environment is the foundation for all human beings, living creatures and ecosystems on this earth. The activities of corporations could not continue without a sound global environment. Recognizing that climate change is a grave challenge faced by the world, the EBARA Group added its signature in endorsement of the TCFD in 2019. Through dialogue with our stakeholders, we will continue to improve our engagement with climate change and our information disclosures.
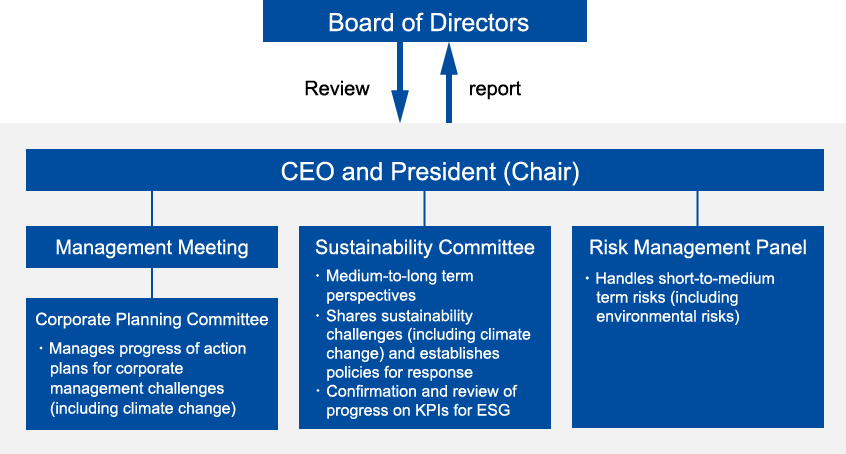
Governance
A risk management panel handles short-to medium term risks. The Corporate Planning Committee, which manages the progress of action plans for corporate management challenges, monitors issues regarding ESG, including climate change, as well as financial aspects.
An Environmental Control Committee, chaired by the executive officers in charge of risk management, has been established as an environmental management framework. We are engaging across the entire Group on a global level on the continuous improvement of environmental management, including climate change response.
Climate Change Governance Structure
Strategy
We followed the following processes in our consideration of the impact of climate change upon the EBARA Group’s businesses.

Identification and evaluation of risks and opportunities of climate change
We identified and evaluated climate-related risks that are likely to affect EBARA Groups’ businesses by 2022, the target year of E-Plan2022, and by 2030, the target year of E-Vision2030. Based on the classification of risks and opportunities specified in the TCFD, we believe that the matters in the table below will have a certain level of impact on EBARA Group’s businesses.
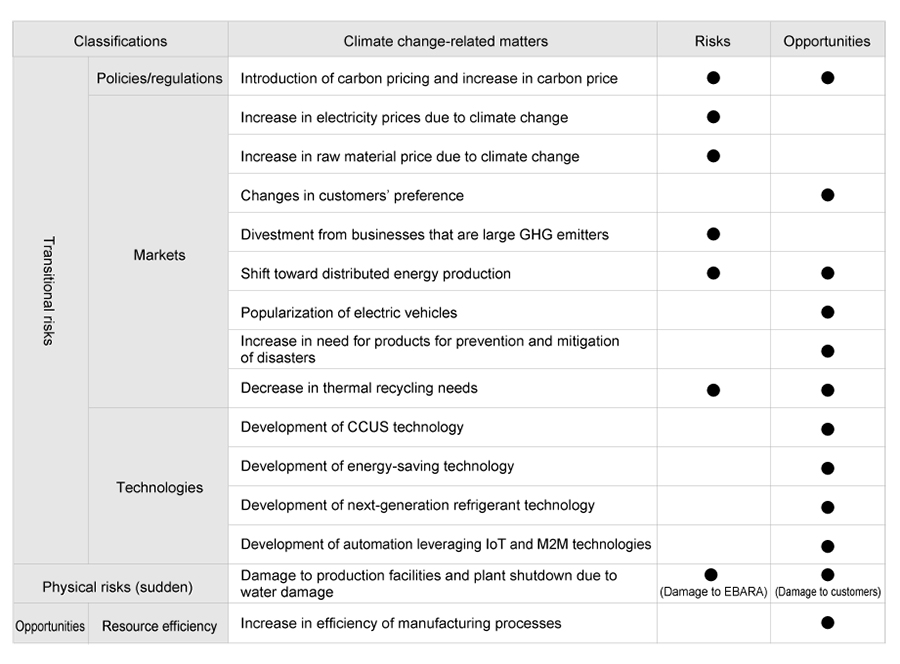
- CCUS:
- Carbon dioxide Capture, Utilization and StorageCarbon dioxide Capture and Utilization (CCU) is a technology that converts captured CO2 into new products and energy.Carbon dioxide Capture and Storage (CCS) is a technology that captures CO2 generated by factories and power stations before it is released into the atmosphere, transports it to geological strata suitable for underground storage, where it is stored in a stable condition for long periods of time.
- GHG:
Greenhouse gases
Scenario Analysis
2-degree scenario
| Category | Major events | Risks | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policies / regulations | Rise in the price of steel, the main raw material for our products | •Increase in manufacturing costs leading to deterioration of earnings •Decline in sales of conventional products that are not environmentally conscious, including CO2 emissions related to manufacturing processes | Increase in sales of GHG-reducing and energy-saving products Growth of LNG-related businesses Growth of precision machinery business |
| Growth in petroleum-alternative energy industries (LNG, etc.) | |||
| Technological innovation | Commercialization of CCUS, greater trend toward energy-saving and high efficiency in pumps and compressors, and commercialization of next-generation refrigerants with lower environmental footprint (green and natural refrigerants) Progress in hydrogen and ammonia-fueled power generation technologies and in hydrogen production and storage technologies | ||
| Market preference | Increased demand by users for carbon-free production due to acceleration of shift toward carbon-free supply chains Increased need for energy-saving products and products that contribute to curbing GHG emissions Shift toward distributed energy production Expansion of popularization of electric vehicles Decline in thermal recycling needs Increase in chemical recycling needs Increased interest in CCUS Increased interest in hydrogen energy |
4-degree scenario
| Category | Major events | Risks | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policies/ regulations | Slight rise in the price of steel, the main raw material for our products Limited impact on petrochemical-related products and increase in customers’ sales among major customers who are likely to be affected by climate policies | •While manufacturing costs will increase due to heavier tax burdens, the impact of earnings will be limited. | No major change in sales compared to 2020 |
| Technological innovation | Stagnation of commercialization of CCUS, greater trend toward energy-saving and high efficiency in pumps and compressors and lack of progress in bringing to market new energy-saving products and services that satisfy consumers’ needs by Ebara and its competitors | ||
| Market preference | Increase in demand for energy-saving products and products that contribute to curbing GHG emissions, albeit at a more moderate rate than under the 2-degree scenario Continued dependence on thermal power generation to a certain extent Increased demand for electric vehicles, albeit at a more moderate rate than under the 2-degree scenario. Continuation of thermal recycling in Japan. |
Midway scenario (2-degree scenario with stagnation of technological innovation)
We assumed a scenario in which policies and regulations are strengthened in a similar way to the 2-degree scenario and customers’ environment-oriented preferences increase, but technological innovation has stagnated and the launch onto the market of products and services that satisfy consumers’ needs is not progressing. Under these circumstances, we believe that sales of energy-saving products and products that contribute to curbing GHG emissions, which can be achieved by the efforts of the EBARA Group, will increase.
| Category | Major events | Risks | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policies/ regulations | Rises in the price of steel, the main raw material for our products, due to the introduction of/increases in carbon pricing. | •Increase in manufacturing costs leading to deterioration of earnings •Decline in sales of conventional products that are not sufficiently environmentally conscious, including CO2 emissions related to manufacturing processes | Increase in sales of energy-saving products and products that contribute to curbing GHG emissions |
| Technological innovation | Stagnation of commercialization of CCUS, greater trend toward energy-saving and high efficiency in pumps and compressors and lack of progress in bringing to market new energy-saving products and services that satisfy consumers’ needs by EBARA and its competitors | ||
| Market preference | Increase in demand for energy-saving products and products that contribute to curbing GHG emissions, albeit at a more moderate rate than under the 2-degree scenario Continued dependence on thermal power generation to a certain extent Increased demand for electric vehicles, albeit at a more moderate rate than under the 2-degree scenario. Continuation of thermal recycling in Japan. |
Common scenario (common risks and opportunities that will manifest in all scenarios)
| Category | Major events | Risks | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policies/ regulations | No common events due to dependence on the degree of strengthening of policies/regulations | •Increase in repair costs accompanying damage to EBARA Group’s facilities Decline in productivity due to more frequent shutdowns caused by temporary disruptions to supply chains (Increase in cost) Decline in sales accompanying decline in major customers’ sales | Demand for IoT and M2M related products and components will increase due to growing momentum for energy conservation through lifecycle from the perspectives of BCP measures and production efficiency improvements, such as yield improvement (resource-saving) and curbing of rework, which will increase sales. Increase in sales due to ability to capture demand for products and maintenance accompanying damage to some customers' factories Increase in sales of products and services for prevention and mitigation of disasters Decline in manufacturing costs due to increase in efficiency of production facilities |
| Technological innovation | Increase in EBARA’s production efficiency in line with updating of production facilities. Expansion of demand for semiconductor-related products required for factory automation, due to production innovation at customers and customers’ BCP measures (prevention of shutdowns due to heat stroke and infectious diseases). | ||
| Market preference | Divestment from businesses that are large GHG emitters and stagnation in petroleum demand Some impact on sales of some customers, such as the oil refining industry Growing need for products that are effective in prevention and mitigation of disasters in light of the frequent occurrence of physical risks such as torrential rains and flooding | ||
| Physical risks | Frequent shutdown of our own and our suppliers’ plants due to water damage such as typhoon, heavy rain, and flooding. Damage to our customers’ facilities (power stations, factory production facilities, public infrastructure such as roads and water supply and sewage systems) due to water damage, requiring their replacement and maintenance. |
- M2M (Machine to Machine):
Machines exchange information with each other over communication networks, thus performing autonomous control and operation to an advanced degree.
- Divestment:
Withdrawal of invested financial assets.
Impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on financial planning
Based on analysis of the four above scenarios, we consider the financial implications climate change by 2030 to be as follows. We predict that none of these scenarios would have significant negative impact on our overall financial position.
| Scenario | Impact on businesses by 2030 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-degree scenario | In response to the strengthening of environmental regulations, progress in CO2-reduction technologies, and growing environmental awareness among consumers, sales of energy-saving products such as pumps, refrigerators, compressors &turbines, and semiconductor manufacturing apparatus, products that contribute to curbing CO2 emission, and chemical recycling-related products will increase. The precision machinery business will grow with the increase in demand for higher efficiency in various industries, due to progress in electric vehicles and digital technologies. On the other hand, business performance will decline due to increases in manufacturing costs caused by rises in the costs of our products’ main raw material and the decline in sales at some of our major customers, due to divestment from businesses that are large GHG emitters. | |||
| Midway scenario (2-degree scenario with stagnation of technological innovation) | While policies and regulations will be strengthened in a similar way to the 2-degree scenario and customers’ environment-oriented preferences will increase, technological innovation will stagnate, and the launch onto the market of products and services that satisfy consumers’ needs will also stagnate. On the other hand, sales of energy-saving products and products that contribute to curbing GHG emissions, which can be achieved by the efforts of the EBARA Group, will increase. | |||
| 4-degree scenario | This is a world positioned as an extension of 2020, with little impact on increases and decreases in sales and expenses brought about by the 4-degree scenario. | |||
| Common to all scenarios | Manifestation of physical risks (e.g., torrential rain, typhoon, high tide, flooding, and drought) will be common to all scenarios. While disaster-caused repair expenses will be incurred, customer demand for maintenance and responses to disasters at public facilities will also be generated, which will lead to increase in sales. Demand for IoT and M2M related products and components will increase due to growing momentum for energy conservation through lifecycle from the perspectives of BCP measures and production efficiency improvements, such as yield improvement (resource-saving) and curbing of rework, which will increase sales. | |||
Strategy based on climate-related risks and opportunities
As a result of analysis of these climate-change scenarios as of 2020, we will focus on the following for our business strategy by 2030. Looking ahead to this, we incorporated them into E-Plan2022.
| Businesses | Strategies until 2030 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid Machinery & Systems Business | Looking ahead to the strengthening of climate-related regulations, increases in raw material prices due to the strengthening of climate-related regulations, and development of divestment from businesses that are large GHG emitters, it will be necessary to consider the development of CCUS and hydrogen and ammonia-fueled power generation technologies, and the formulation of strategies for new businesses such as hydrogen production and storage technologies. | ||
| Environmental Engineering Business | In response to increase in customers’ environment-oriented preferences, it will be necessary to respond to advanced recycling needs, such as chemical recycling of waste plastics. | ||
| Precision Machinery Business | Promote development of products that contribute to energy-saving needs through product lifecycle, to automation needs that leverage IoT and M2M technologies as highly efficient production systems, and to the shift from petroleum-fueled vehicles to electric vehicles. | ||
| EBARA Group’s general production activities | As customers are expected to demand a shift toward carbon-free supply chains, it will be necessary to consider cutting CO2 emissions generated from manufacturing processes. | ||
Risk management
Metrics and Targets
In E-Plan2022, we developed action plans for both financial and non-financial corporate management challenges, which set metrics and targets to manage the progress of these action plans. The non-financial action plans set metrics and targets for risks and opportunities regarding environment, including climate change, society, and governance. The Sustainability Committee and Corporate Planning Committee monitor progress of these plans.
Sustainability Menu
EBARA's Sustainability
Sustainability Data
Governance
Environmental
Social
Social Contribution
Inquiry about sustainability